| 1. |
EPA water quality criteria guidance includes some components for each regulated pollutant. They are: |
|
|
Magnitude (the allowed concentration in ambient water) |
|
|
Duration (the averaging period over which the ambient pollutant concentration is compared to the allowed value) |
|
|
Frequency (how often the criterion may be exceeded) |
|
|
All of the above |
| 2. |
Mixing zone implementation differs widely across the United States. Some states have very prescriptive policies and procedures for establishing mixing zones and calculating dilution factors. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 3. |
What does USGS stand for? |
|
|
United States Geological Survey |
|
|
United Standard Geological Survey |
|
|
None of the above |
|
|
United States Geological Standard |
| 4. |
The harmonic mean flow used to evaluate ambient water quality against human health criteria is a long-term mean value for the receiving water calculated according to procedures outlined by Rossman and EPA. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 5. |
After determining effluent dilution under critical conditions for a bay or estuary,
EPA (1991) also recommends checking a non-critical condition (e.g., higher river inflow or lower stratification) that encompasses the period of maximum ambient velocity during a tidal cycle.
|
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 6. |
EPA’s minimum requirement is that water quality within mixing zones should result in lethality to migrating fish, drifting organisms moving through a plume, or sessile organisms that may attempt to reside within a mixing zone. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 7. |
States fall into two categories with regard to the overall process of establishing mixing zones. In the first category, a state sets the dimensions of the mixing zone and calculates dilution factors for the discharger. The second category of states require the discharger to submit a mixing zone study which establishes the dilution factor. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 8. |
What does table 2-1 illustrate about? |
|
|
Mixing Zone Regulations of Selected States |
|
|
Florida Department of Environmental Protection |
|
|
Permitting Authority |
|
|
None of the above |
| 9. |
The results of the reasonable potential analysis are also used to determine the maximum size of the mixing zone. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 10. |
The physics of effluent mixing and dilution involve the principles of conservation of mass, momentum, and energy. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 11. |
What does figure 3-1 illustrate about? |
|
|
Illustrations of Plumes and Jets |
|
|
Pure Plume in uniform crossfire |
|
|
Effects of ambient conditions on discharge |
|
|
None of the above |
| 12. |
Negatively buoyant discharges will rise regardless of discharge hydraulics until reaching the surface or entraining sufficient ambient water to equal the density of the receiving body |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 13. |
The term "outfall pipe" is typically used to refer to the pipe extending from the wastewater treatment plant to the first port. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 14. |
Lateral mixing in rivers occurs over relatively longer distances and is dependent on factors such as current speed, channel morphology, and the presence or absence of bottom roughness and rapids. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 15. |
For buoyant discharges, research has shown that the dilution of a multi-port diffuser in un-stratified waters increases in proportion to the length raised to the 2/3 powers, as indicated below
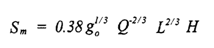
What does Q stand for in the above equation?
|
|
|
Design discharge rate |
|
|
Tube coefficient |
|
|
Height of the tube |
|
|
None of the above |
| 16. |
Peak flow conditions must be evaluated to ensure that sufficient head exists to discharge effluent at the design high water level without adversely impacting treatment plant hydraulics. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 17. |
Risk of infrastructure damage can come from causes including storms, currents, shipping, seismic failures, debris, sediment, and plant growth. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 18. |
One-dimensional models consider changes in pollutant concentration over a single dimension in space, typically the axis of the discharge jet or plume |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 19. |
Steady state models predict receiving water concentrations in response to model inputs (e.g., effluent flows, concentrations) that remain constant over time. |
|
|
True |
|
|
False |
| 20. |
A more rigorous tool is available for predicting maximum in-stream concentrations downstream of a discharge as well as attenuation due to ambient dilution. This desktop equation is:
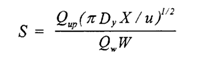
What does W stand for in the above equation?
|
|
|
Stream width |
|
|
Discharge |
|
|
Diameter of the tube |
|
|
None of the above |
|